|
|||||||||

Comments
Peaks
that are double, fronting, tailing, or very broad are almost always caused
by a column or guard column that is obstructed, contaminated, or worn
out.
The chance for artifacts caused by using a sample solvent that is different from the mobile phase is greater when the sample volume is relatively large. For example, when using an analytical reversed phase column, a mobile phase of 30% methanol in water and a sample dissolved in pure methanol, distortion may be absent when injecting 10 µL, but present when injecting 50 µL.
When using gradient elution, broad peaks that elute among the otherwise normal appearing peaks can be highly retained peaks from the previous injection(s). This is caused by not programming the mobile phase to a high enough strength and/or not holding it at a sufficient strength for long enough. This can be confirmed by programming to 100% of the strongest mobile phase, after the peaks of interest have eluted, and holding at this composition until no more peaks elute. Then, after equilibrating a sufficient time with the initial mobile phase (e.g., five column volumes), inject the next sample and observe the chromatogram.
Symptom #6
Peaks are distorted — fronting, tailing, or very broad — and a blank injection is free of peaks. The injector cannot malfunction to cause such symptoms. Check for the following:
- If the
sample solvent is not mobile phase, see Cause A. Otherwise,
connect a different column which did not previously produce the symptoms:
- If the symptoms are now absent, see Cause B.
- If the symptoms are still present, see Cause C.
Cause A
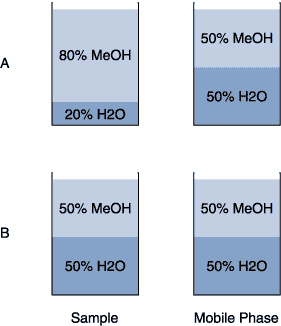
Sample solvent that is stronger than mobile phase (see Fig. 22) causes unsymmetrical early peaks, especially with a large sample volume.Solution
Use mobile phase for the sample solvent or use a smaller sample volume. If not practical, use a solvent that is as similar as possible.
Fig. 22. A sample solution (A) that may cause artifacts and one (B) that will eliminate them.
Cause B
The column or guard column is defective.Solution
Clean or replace the column or guard column.Cause C
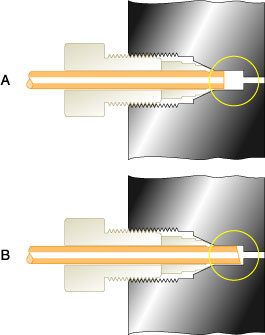
Loop or column tube connections may have a dead volume (see Fig. 23), causing tailing.Solution
All tubing should be square cut and bottomed in the ports. Replace the loop or column connecting tubes if necessary.
Fig. 23. Poor connections result if tubing is not bottomed in the port (A) or is not cut square (B).
© 2000 Rheodyne All rights reserved